Prototyping
Make Your Data
Work For You
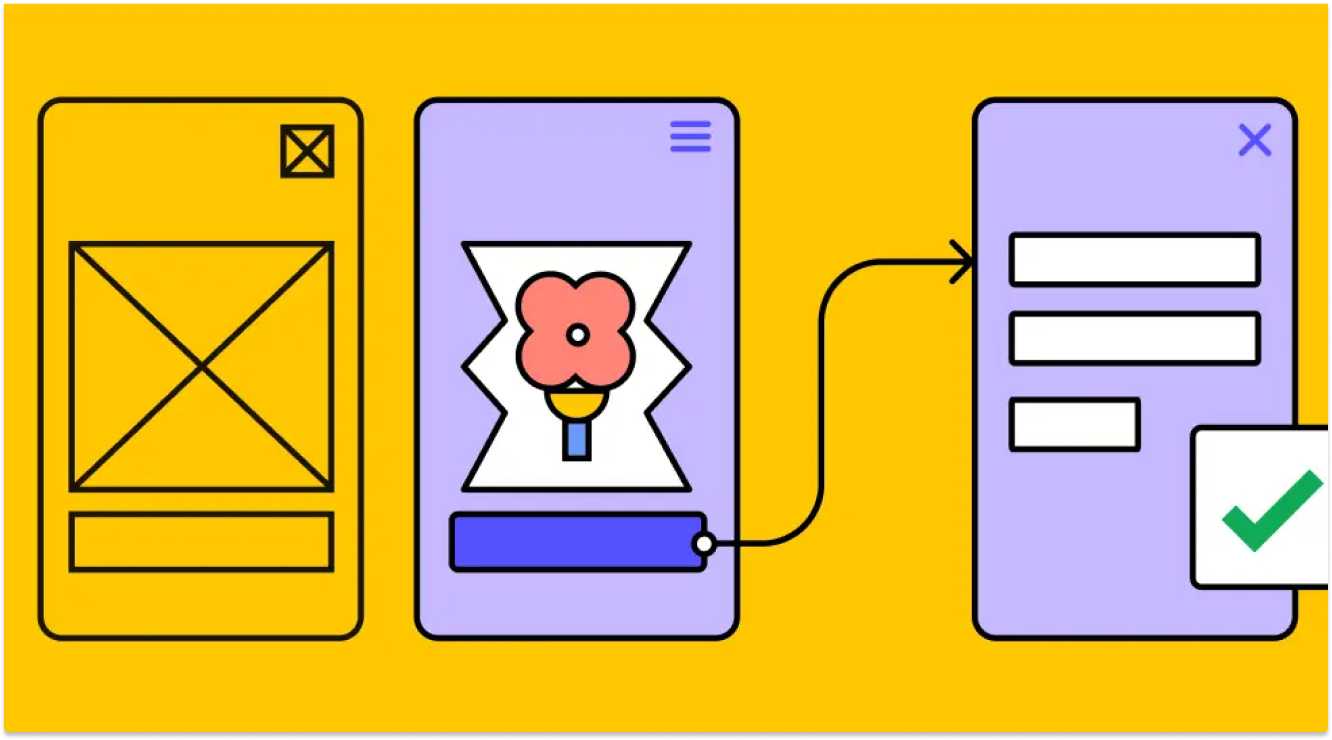
What is Prototyping?
Here's a breakdown of what prototyping involves:
1. Conceptualization:
The prototyping process typically begins with brainstorming and conceptualization. This stage involves defining the goals and objectives of the product, identifying the target audience, and outlining the key features and functionalities.
2. Design:
Once the concept is established, designers create mockups or wireframes of the product's user interface (UI) and user experience (UX). These visual representations help stakeholders visualize the product's layout, navigation, and interactions.
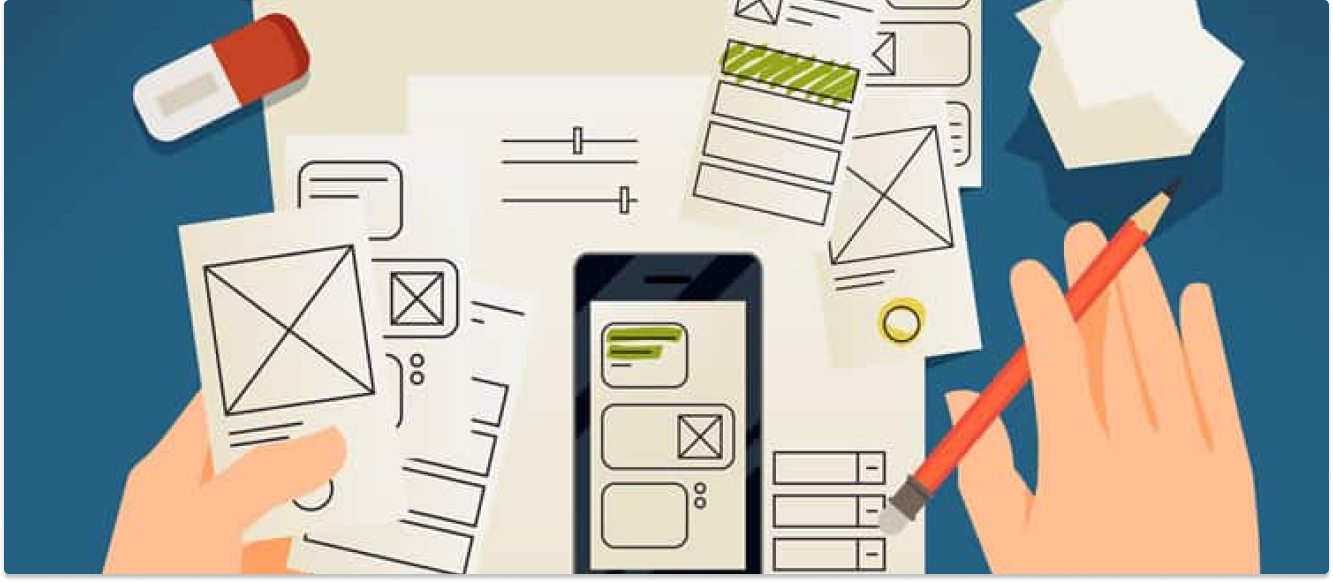
3. Low-Fidelity Prototypes:
Low-fidelity prototypes are basic representations of the product, often created using pen and paper or digital tools like Balsamiq or Sketch. These prototypes focus on the overall structure and flow of the product without detailing specific design elements.
4. Feedback and Iteration:
Low-fidelity prototypes are presented to stakeholders, including potential users, for feedback and validation. This feedback is used to refine the prototype through iterations, addressing any usability issues or design flaws identified during testing.
5. High-Fidelity Prototypes:
High-fidelity prototypes are more detailed and closely resemble the final product in terms of design and functionality. These prototypes may be interactive, allowing users to navigate through different screens and perform basic tasks.
6. User Testing:
High-fidelity prototypes are subjected to rigorous user testing to evaluate how users interact with the product and identify any usability issues or pain points. This feedback is invaluable in refining the product further and ensuring it meets the needs and expectations of the target audience.
7. Validation:
Once the prototype has undergone sufficient testing and refinement, it is validated against the original goals and objectives established during the conceptualization phase. This validation helps ensure that the prototype aligns with the business objectives and is ready for further development or production.
8. Documentation:
Throughout the prototyping process, it's essential to document all changes, feedback, and decisions made. This documentation serves as a reference for future iterations and helps maintain consistency and clarity throughout the development process.